Tool
Lobby and advocacy cycle
Effective advocacy requires a well-structured approach, especially when addressing complex issues like sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) through an intersectional lens. Explore the steps outlined below to navigate your advocacy journey, ensuring that your efforts are inclusive, impactful, and sustainable.
Table of content
1. Before you start
2. Analysing the issue
3. Setting advocacy goals and objectives
4. Coalition building
5 . Stakeholder and power mapping
6. Developing an advocacy plan
7. Creating a communication and media strategy
8. Time for implementation
9. Monitoring, evaluation and learning
Additional material
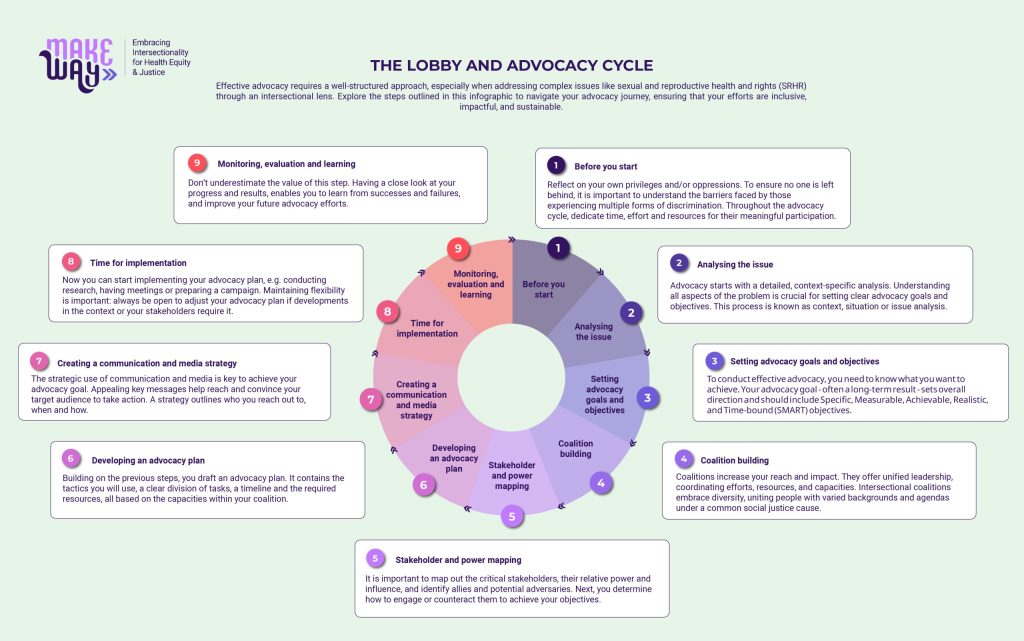
1. Before you start
Reflect on your own privileges and/or oppressions. To ensure no one is left behind, it is important to understand the barriers faced by those experiencing multiple forms of discrimination. Throughout the advocacy cycle, dedicate time, effort and resources for their meaningful participation.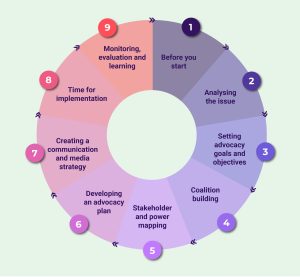
2. Analysing the issue
Advocacy starts with a detailed, context-specific analysis. Understanding all aspects of the problem is crucial for setting clear advocacy goals and objectives. This process is known as context, situation or issue analysis.
3. Setting advocacy goals and objectives
To conduct effective advocacy, you need to know what you want to achieve. Your advocacy goal – often a long-term result – sets overall direction and should include Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound (SMART) objectives.
4. Coalition building
Coalitions increase your reach and impact. They offer unified leadership, coordinating efforts, resources, and capacities. Intersectional coalitions embrace diversity, uniting people with varied backgrounds and agendas under a common social justice cause.
5 . Stakeholder and power mapping
It is important to map out the critical stakeholders, their relative power and influence, and identify allies and potential adversaries. Next, you determine how to engage or counteract them to achieve your objectives.
6. Developing an advocacy plan
Building on the previous steps, you draft an advocacy plan. It contains the tactics you will use, a clear division of tasks, a timeline and the required resources, all based on the capacities within your coalition.
7. Creating a communication and media strategy
The strategic use of communication and media is key to achieve your advocacy goal. Appealing key messages help reach and convince your target audience to take action. A strategy outlines who you reach out to, when and how.
8. Time for implementation
Now you can start implementing your advocacy plan, e.g. conducting research, having meetings or preparing a campaign. Maintaining flexibility is important: always be open to adjust your advocacy plan if developments in the context or your stakeholders require it.
9. Monitoring, evaluation and learning
Don’t underestimate the value of this step. Having a close look at your progress and results, enables you to learn from successes and failures, and improve your future advocacy efforts.
Lobby and advocacy cycle
10. Additional material
Your questions and suggestions:
"*" indicates required fields


